© Copyright 2018. All Rights Reserved.
Introduction
Hypothyroidism can significantly affect someone's overall health. In addition to its potential to affect fertility, this condition has other lesser-known consequences. As we explore this link in some depth, we will be able to help those struggling with infertility understand the intricate relationship between hypothyroidism and infertility.
An Overview of the Thyroid Gland
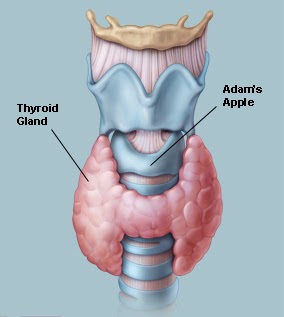
Understanding the thyroid gland's role in our bodies is essential before we delve into hypothyroidism and infertility. This butterfly-shaped gland is found at the base of the neck and plays a crucial role in regulating our metabolism. T4 (thyroxin) and T3 (triiodothyronine) are the two hormones produced by it. The hormones are responsible for regulating many functions in the body, including the way the body uses energy, the way it generates heat, and how other organs are affected.
What is the Thyroid Gland?
Here are some basics to get you started. A single lobe of the thyroid gland is connected to the other by an isthmus. Thyroid glands have a unique structure that gives them a butterfly-like appearance, which is important to the aesthetics of their appearance. Our metabolism is kept in check through a remarkable array of processes conducted within this small but mighty organ.
Metabolic Function of the Thyroid
Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are the two essential hormones produced by the thyroid gland to oversee metabolism. A wide range of vital functions are influenced by these hormones in almost every cell of the body:
Regulatory Functions: The thyroid hormones regulate energy metabolism, which in turn determines the amount of energy spent at rest, called our basal metabolic rate (BMR). Weight loss and heat intolerance can be symptoms of an overactive thyroid, while fatigue and weight gain can be symptoms of an underactive thyroid.
Thyroid Function: This gland influences heat production and thermoregulation in order to keep the body at a constant temperature. Sweating and heat intolerance are signs of an overactive thyroid, whereas a sluggish thyroid causes sensitivity to cold.
Blood Pressure : Thyroid hormones directly affect cardiovascular health and heart rate. A rapid heartbeat is a sign of hyperthyroidism, while a slow heartbeat is a sign of hypothyroidism.
Diseases of the thyroid gland
There are several disorders that can disrupt the functioning of the thyroid, regardless of its vital role:
Thyroid hyperfunction: Rapid heartbeat, weight loss, anxiety, and tremors are some of the side effects caused by an overactive thyroid gland.
A hypothyroid condition: Hyperthyroidism is the opposite condition when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Cold sensitivity, fatigue, weight gain, and depression are a few symptoms to look out for.
Inflammatory Nodules: The thyroid gland may develop benign or malignant tumors due to inflammation due to abnormal growths. As a result, the thyroid function may change or remain asymptomatic.
Diseases Affecting the Thyroid: Thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease are caused by autoimmune conditions. Graves' disease results in hyperthyroidism, while Hashimoto's disease results in hypothyroidism.
Managed and treated
Medications are typically prescribed to treat thyroid disorders. A hyperthyroid patient may benefit from antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery to remove part of their thyroid. The most effective way to treat hypothyroidism is to use synthetic thyroid hormones, such as levothyroxine, to replace the thyroid hormones.
Hypothyroidism overview
An individual with hypothyroidism produces insufficient thyroid hormones, principally T4 and T3. There are many symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances, including fatigue, weight gain, thinning hair, and sensitivity to cold. Women and men can both suffer infertility due to hypothyroidism, despite these symptoms being challenging on their own.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
There are two main types of hypothyroidism: benign and malignant.
-
Hypothyroidism (Primary) : This is the most common type of hypothyroidism and occurs when the thyroid gland itself doesn't function properly. Radiation therapy or surgical removal of the thyroid gland are other causes, as well as autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
- Hypothyroidism in secondary form : This form of hypothyroidism is caused when the pituitary gland or hypothalamus do not function properly. The pituitary gland is responsible for regulating the thyroid's production of hormones. Symptoms of thyroid hormone production decrease if the brain structures are damaged by tumors or injuries, or by certain medications.
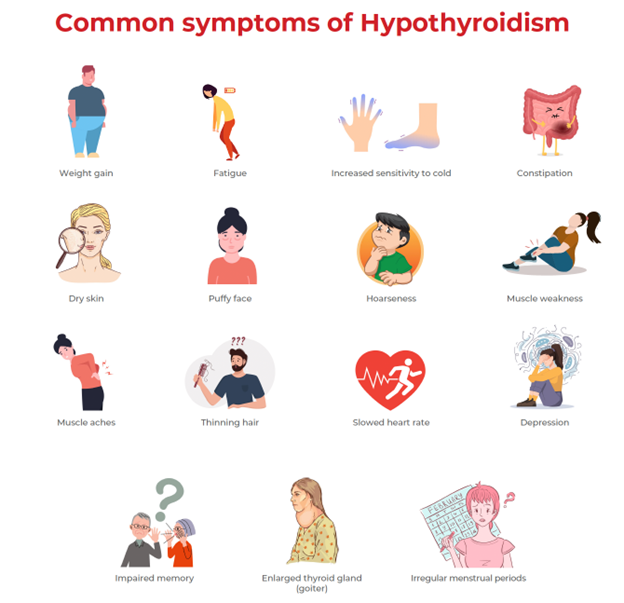
There are many symptoms of hypothyroidism, which can vary from one person to the next. Symptoms that are common include:
- Deficiency and fatigue
- Intake of calories
- Intolerance to cold
- Intense dryness
- Lack of hair
- Pain in joints and muscles
- Digestion problems
- Women's irregular menstrual cycles
- Hypercholesterolemia
Treating and diagnosing
Blood tests are usually used to diagnose hypothyroidism by measuring thyroid hormone levels (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels (TSH). Hypothyroidism is characterized by high TSH levels and low levels of T3 and T4.
It is vital to replace thyroid hormones in the treatment of hypothyroidism. In order to supplement inadequate thyroid hormone production, patients commonly receive synthetic thyroid hormones, such as levothyroxine. Treatment for hypothyroidism involves restoring normal thyroid hormone levels in the body, alleviating symptoms.
Infertility in Females with Hypothyroidism
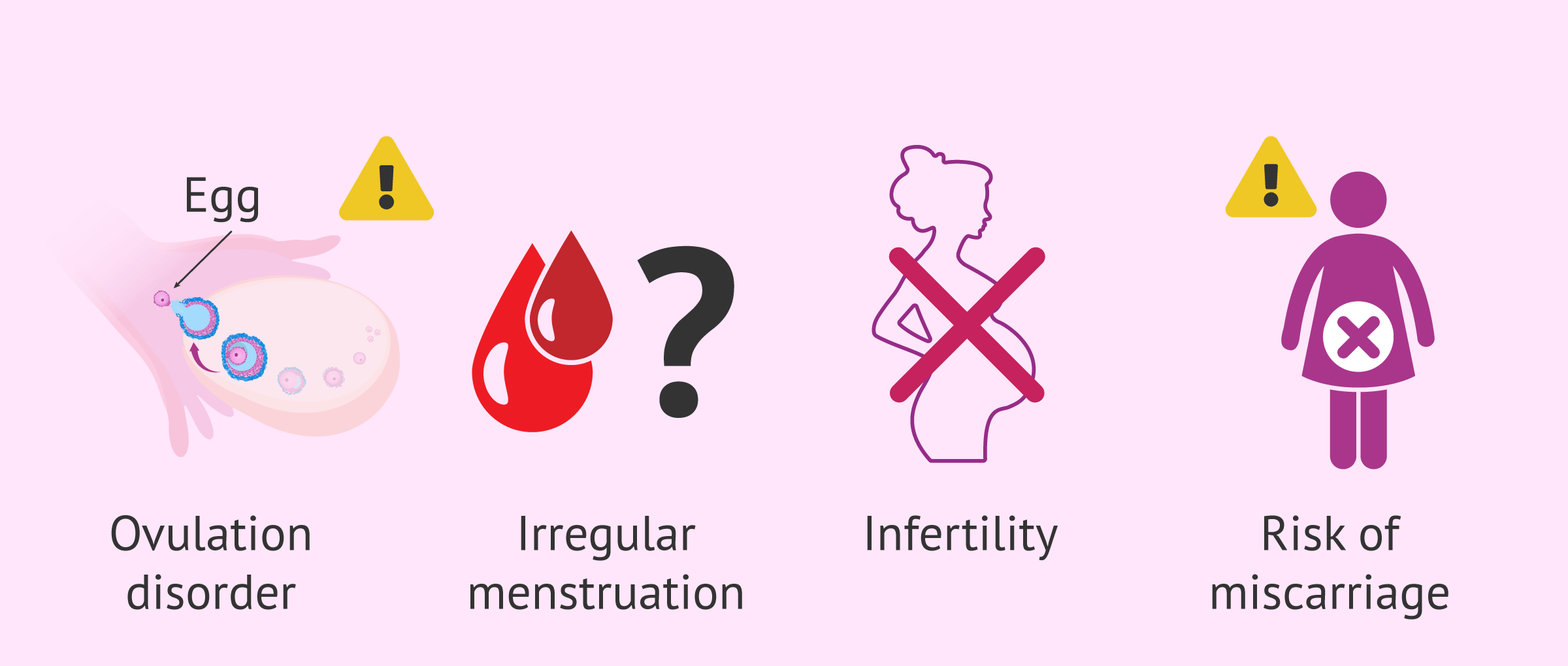
Menstrual cycle and ovulation are both affected by hypothyroidism in women. In the absence of optimal thyroid function, women can experience irregular periods, anovulatory disorders, and other ovulatory problems. A woman's ability to get pregnant is hindered by these issues.
Because hypothyroidism prevents the body from producing the necessary hormones for a healthy pregnancy, hypothyroidism can also affect a hypothyroid pregnancy. In addition to causing miscarriages, it can also lead to complications during pregnancy. It is important to examine and treat the thyroid function of these women if they are trying to become pregnant.
Inconsistency of Menstruation: Women that suffer from hypothyroidism experience irregular menstrual cycles, which make it difficult to predict ovulation, a crucial factor in conception.
Anovulation: Hypothyroidism may cause ovaries to fail to release eggs during the menstrual cycle, further complicating pregnancy attempts.
Interruption of Ovulatory Process: Thyroid hormone imbalances can interfere with the production of other reproductive hormones, including follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) and luteinizing hormones (LH).
How to treat hypothyroidism for fertility
Many women with hypothyroidism can improve the chances of becoming pregnant with proper treatment and management. Steps to consider:
Examine Your Health: Consult a doctor to determine whether you need further evaluation. There are several blood tests that can provide insight into thyroid function. They include thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), and triiodothyronine (T3).
Optimizing Thyroid Function: This is the key to having a healthy thyroid. In many cases, replacement of thyroid hormones is accomplished through medication, such as levothyroxine.
Maintain Healthy Hormone Levels: Regular doctor's appointments and thyroid function tests are important in maintaining a healthy hormone level.
Lifestyle and Nutrition: Eat a healthy diet rich in nutrients for thyroid health. Overall well-being can also be improved by regular exercise and stress management techniques.
Infertility Treatment: Consult an endocrinologist or fertility specialist if fertility struggles persist. Assistive reproductive technology or fertility treatment are some of the specialized interventions they can offer.
Support and well-being in emotional areas
Emotions can be taxing when facing fertility challenges. This journey involves emotional aspects that must be acknowledged and supported. In times of stress, talking to someone who has been through a similar experience can be extremely helpful.
Male infertility due to hypothyroidism
Its effects on female fertility aren't the only ones caused by hypothyroidism. Infertility can also be a consequence of it in men. Testosterone, which plays a critical role in sperm production and quality, is regulated by thyroid hormones. Lower testosterone levels can result in decreased sperm counts and sperm motility when the thyroid is underactive.
Male infertility and hypothyroidism have complex and multifaceted relationships, involving several factors.
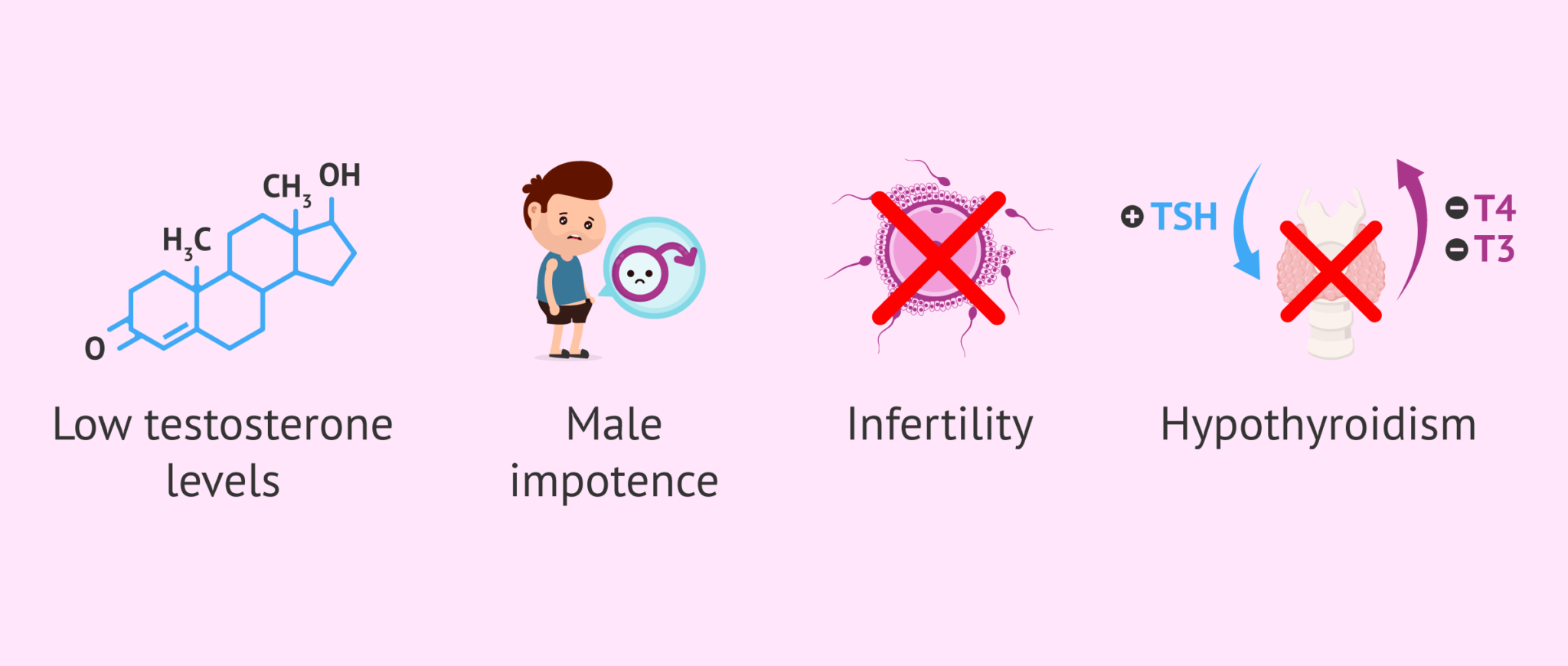
1. Imbalanced hormones: Hyperthyroidism disrupts healthy hormonal balance required for healthy sperm production. Sperm production relies on testosterone levels, the male sex hormone, which thyroid hormones regulate.
2. Quality of Sperm: Due to hypothyroidism, sperm morphology (shape and structure) and motility (movement) may be changed, resulting in reduced sperm quality. Fertility may be negatively affected.
3. Sexual Function: Erectile dysfunction and decreased libido are also symptoms of hypothyroidism and can impair conceiving.
Providing treatment and diagnosis
The first step to addressing male infertility is to diagnose and treat hypothyroidism. Steps to be taken are as follows:
1. Diagnostic Test: See an endocrinologist or healthcare practitioner. Testing for thyroid hormone levels can be performed with blood tests, including thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), and triiodothyronine (T3).
2. Replacement of thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is usually used to treat hypothyroidism. Thyroid hormone levels are generally restored by medications such as levothyroxine.
3. Blood Tests: It is essential to maintain healthy thyroid hormone levels through regular follow-up visits and thyroid function tests.
4. Nutrition and Lifestyle Support: Being healthy and eating a balanced diet can help support overall well-being.
Guidance from experts
A reproductive endocrinologist or fertility specialist may be able to help if fertility struggles persist despite hypothyroidism treatment. Male infertility caused by thyroid difficulties can be treated with specialized treatments, including intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Supporting your emotions
Men who are infertile can have an emotional journey, and it's essential to identify and understand these aspects. If you're struggling to cope with the emotional toll of fertility struggles, find support from a therapist, counselor, or support group.
A solution and a treatment
Good news! Hypothyroidism can frequently be managed successfully and has a positive impact on fertility. A healthcare professional should be consulted if you suspect thyroid issues may be affecting your fertility. Thyroid hormone levels are usually checked with a simple blood test.
Usually, thyroid hormone replacement therapy is the treatment of choice if hypothyroidism is diagnosed. Fertility issues can often be resolved when hormone levels return to balance, and many women are well positioned to conceive when hormone levels are restored.
Conclusion
People trying to start or expand their families should understand the link between hypothyroidism and infertility. People can address thyroid troubles and enhance their chances of successfully conceiving if they become aware of the symptoms and seek proper medical attention. Talk to your healthcare provider if you suspect hypothyroidism is interfering with fertility. They can help you find a healthy and fulfilling family life.
Recent Post
-

Intrauterine insemination (IUI) Success Tips: Enhance Your Fertility
-

The Connection Between HCG Hormone and Pregnancy: Explained in detail
-

Conquering Asthenozoospermia: Strategies for Male Fertility Success
-
Embracing Sensuality with Vaginismus: Strategies and Support
-
Understanding Endometriosis: Symptoms, Causes & Management | Guide